.jpg)
区块链是什么呢?笔者认为是“账本”。
What's the block chain? I think it's & ldquao; account book & rdquao;
打个比方,A向B借了100元。账本上,就会记下某年某月,A向B借了100元。然后这个账本是共享的,大家都会在这个账本上记录某年某月A向B借了100元。最后,这个账本是不能修改的,信息传输是有安全机制保障的。
For example, A borrows $100 from B. On a book, A borrows $100 from B a month, and A borrows $100 from B a month. Then this book is shared, and everyone borrows $100 from B a month of the year. Finally, the account book is unmodifiable, and the transmission of information is secured by a secure mechanism.
为什么叫区块链呢?我分成两部分解释,一个是区块,一个是链。
Why is it called a block chain? I explained it in two parts, one block and the other chain.
区块链技术把共享账本(类似分布式数据库)中需要存储的数据分成了不同的区块,每个区块通过特定的信息链接到上一区块的后面,前后按时间顺序连接起来呈现一套完整的数据。每个区块链的分布式账本从本质上讲是一个按照时间顺序串联起来的事件链,它使用协议规定的密码机制进行了认证,保证不会被篡改和伪造。
Block chain technology divides the data to be stored in a shared account book (a similarly distributed database) into different blocks, each linked by specific information to the back of the previous block, with a complete set of data attached in chronological order. The distributed account book for each block chain is essentially an event chain linked in chronological order, certified using the password mechanism provided by the protocol to ensure that it is not altered and falsified.
1.区块结构
1. Block structure
区块是使用密码学方法产生的数据块,数据以电子记录的形式被永久储存下来,存放这些电子记录的文件我们就称之为“区块(block)”。以比特币的区块链为例,它完整记录了网络上的每一笔历史交易,好比是一个银行账本。每个区块记录了这几个内容:神奇数、区块大小、数据区块头部信息、交易计数、交易详情。
Blocks are data blocks generated using cryptographic methods that are permanently stored in electronic records, which we call “ block (block) & rdquo; and, for example, bitcoin's block chain, which provides a complete record of every historical transaction on the network, as if it were a bank account. Each block records these elements: magic numbers, block size, data block head information, transaction count, transaction details.
2.区块链结构
2. Block chain structure
每一个区块都由块头和块身组成。块头用于链接到上一个区块的地址,并且为区块链数据库提供完整性的保证。块身则包含了经过验证的、块创建过程中发生的交易详情或其他数据记录。
Each block consists of a block and a block. The block is used to link the address of the previous block and to provide assurance of the integrity of the block chain database.
区块链的数据存储方式通过两个方式来保证数据库的完整性和严谨性。第一,每一个区块上记录的交易是上一个区块形成之后、该区块被创建前发生的所有价值交换活动,这个特点保证了数据的完整性。第二,在绝大多数情况下,一旦新区块完成后被加入到区块链的最后,则此区块的数据记录就再也不能改变或删除。这个特点保证了数据的严谨性,即无法被篡改。
The data storage of the block chain ensures the integrity and rigour of the database in two ways. First, the transaction recorded on each block is all value swaps that occur after the formation of the previous block and before the block was created, a feature that guarantees the integrity of the data. Second, in most cases, once the new block is completed and added to the end of the block chain, the data records of the block can no longer be altered or deleted. This feature guarantees the rigour of the data, that is, it cannot be tampered with.
3.链式结构
3. Chain structure
区块和区块之间是如何“链”起来的呢?主要依靠各个区块之间的数据区块头部信息链接起来,头部信息记录了上一个区块的HASH值(通过散列函数变换的散列值)和本区块的HASH值。本区块的HASH,又在下一个新的区块中有所记录,由此完成了每个区块的信息链。
How do blocks and blocks & & & ldquo; chains & & rdquo; get together? The data block head information is mainly linked between blocks, where head information records the HSH value of the previous block (a hash value converted through a hash function) and the HSH value of the present block. The HSH of this block, again recorded in the next new block, completes the information chain for each block.
同时,由于包含了时间戳,区块链还带有时序性。时间越久的区块后面所链接的区块越多,修改该区块所花费的代价也就越高。区块链采用了密码协议,允许计算机(节点)的网络共同维护信息的共享分布式账本,而不需要节点之间的完全信任。
At the same time, because of the time stamp, the block chain is time-series. The more blocks are linked behind a block, the higher the cost of modifying the block. The block chain uses a password protocol that allows computer networks (nodes) to jointly maintain shared distribution books of information without the need for full trust between nodes.
区块链不是万金油
我的第一个观点是:区块链不是万金油,也不是银弹,不能解决物流行业面临的问题,比如双11快递爆仓、路由优化等。从根本上说,这些问题与区块链没有直接的关系,区块链也不是用来解决这些问题的。 My first point is that the block chain is not gold oil, it is not silver bullets, and it does not solve the problems facing the logistics industry, such as double-11 delivery silos, route optimization, and so on. Basically, these problems are not directly related to the block chain, and the block chain is not meant to solve them. 因为区块链技术还在发展中,其本身作为一种分布式的技术,业务处理上是适合的,可是由于技术的发展是一个从1.0到2.0到3.0的过程,所以,有些场景本身适合,但现阶段技术的发展并未达到。这里用3个例子来说明。 Because block chain technology is still developing and is itself appropriate as a distributed technology, but because technology development is a process from 1.0 to 2.0 to 3.0, some scenes are appropriate in themselves, but at this stage technological development has not been achieved. Three examples are used here. 1.交易效率低 1. Inefficiency of transactions 目前行业区块链的交易数,对多个节点的共识,交易速度是很慢的。 At present, the number of transactions in the industry block chain is very slow in terms of consensus on multiple nodes. 2.去中心化悖论 2. Decentralization paradox 就国内情形来看,区块链技术还未获得监管部门的某些方面的认可,所以更准切的说是要多中心化。 In the domestic context, block chain technology has not been recognized by some quarters of the regulatory authorities, so it is more pertinent to say multi-centric. 3.安全问题 3. Security issues 1.0时,一个节点交易,另外其他节点也能看到此交易。所以,对于企业而言,这个技术是不安全的。我和某个人之间的交易,我不希望其他人看到,除非我们有一种授权机制,所以技术本身的成熟度可能阻碍了它的发展。 At 1.0 a.m., a node deal, and other nodes can see it. So, for a business, this technology is not safe. I don't want anyone to see it unless we have an authorization mechanism, so the maturity of the technology itself may impede its development. 所以说,区块链技术不是万能的,目前的区块链技术成熟度和业务需求存在差距。比如说不适用的场景就有:高性能交易(大量交易)、仅有有一名参与者的交易(区块链一定是多个参与者参与的商业网络)、寻找数据库的替代方案、寻找消息传递的解决方案、寻找交易处理的替代方案、低价值大容量的交易等等。 So block chain technology is not all-powerful, and there are gaps in current block chain technical maturity and business needs. For example, high-performance transactions (a large number of transactions), transactions with only one participant (a segment chain must be a commercial network involving multiple participants), alternatives to finding a database, solutions to find a message, alternatives to transaction processing, low-value high-volume transactions, etc., are not applicable. 区块链的特点是什么? What are the characteristics of the block chain? 1.共享账本 1. Shared books of accounts 它是一个分布式数据库的概念。交易记账由分布在不同的多个节点共同完成,而且每一个节点都记录的是完整的账目,因此他们都可以参与监督交易合法性,同时也可以共同为其作证。就像刚才举得例子,A向B借了100元这件事情所有人都可以为其作证。理论上讲,除非所有人的账目都被破坏,否则A向B借了100元这件事情不会赖掉。 It is the concept of a distributed database. The transaction logs are carried out by multiple nodes, and each node records a complete account, so that they can be involved in monitoring the legitimacy of the transaction, and they can testify against it together. As we just mentioned, A borrows $100 from B, for which everyone can testify. In theory, A borrows $100 from B unless everyone’s accounts are destroyed. 2.智能合约 2. Smart contracts 智能合约就是可以在区块链环境下执行的一段程序代码。它是基于可信的、不可篡改的数据,可以自动化地执行一些预先定义好的业务规则和商业条款。比如A向B借了100元,可以写一段智能合约的代码完成某种条件下的自动还款。如果至2月10日,A没有还B 100元,A账户自动向B账户转100元。到了2月10日,外部事件定时器会自动触发智能合约上的这段程序代码,转账自动产生,这就是智能合约的概念。 A smart contract is a program code that can be implemented in a block chain environment. It is based on credible and non-manual data that allows for automated implementation of predefined business rules and commercial provisions. For example, A borrows $100 from B to write a code for a smart contract to complete an automatic repayment under certain conditions. If A does not pay B $100 by February 10, A automatically transfers $100 to B accounts. By February 10, the external event timer automatically triggers this program code on the smart contract and transfers automatically occur, which is the concept of a smart contract. 3.隐私保护 3. Privacy protection 区块链上的交易信息是公开的,但是账户身份信息是高度加密的。只有在数据拥有者授权的情况下才能访问到,从而保证了数据的安全和个人的隐私。 The transaction information on the block chain is publicly available, but the account identification information is highly encrypted. 4.共识机制 4. Consensus mechanism 所有节点之间需要采用一种共识机制从技术保证节点之间对共享账本信息如何达成共识,去认定一个记录的有效性,这既是认定的手段,也是防止篡改的手段。所有参与者一致同意,才意味着交易在网络中通过验证,从而杜绝了造假的可能。 There is a need for a consensus mechanism between all nodes to determine the validity of a record by agreeing on how to share account information between the nodes of the technical assurance, both as a perceived tool and as a means of preventing tampering. All participants agree that this means that the transaction is validated in the network, thereby eliminating the possibility of forgery. 区块链的应用场景 field of application of block chains 我的第二个观点是:快递物流行业是非常适合应用区块链技术的行业。 My second view is that the express logistics industry is well suited to the application of block chain technology. 实际上,物流生态系统是有多个参与方组成的利益共同体。行业内有一个关于「流」的概念,从最初的「商流」开始,逐渐催生出「物流」,以及相对应的「资金流」和「信息流」的支撑。 In fact, the logistics ecosystem is a multi-participating interest community. There is a concept of "flow" in the industry, starting with the initial "business stream" that has led to the emergence of "logistics" and the support of corresponding "financial flows" and "information flows". 各种「流」的产生,其背后都有一个关键问题,就是一个商品所有权的转移。区块链技术解决的问题类型很多是和资产所有权进行转移过程中产生的信任摩擦相关。因此,可以得出这样的结论,快递物流行业中的涉及的多流融合的业务场景非常适合区块链技术发挥它的价值和效果。 应用区块链技术可以显著提高快递物流行业中结算业务的处理速度及效率,有效解决物品的追溯防伪问题,充分保证信息安全以及寄、收件人的隐私。下面,我列举出四种适合区块链技术的快递物流行业的业务场景类型。 As a result, it can be concluded that the multi-stream business scenes involved in the express logistics industry are well suited to the value and effectiveness of block chain technologies. The application of block chain technologies can significantly improve the speed and efficiency of settlement operations in the express logistics industry, effectively address the issues of retroactive forgery of goods, and adequately guarantee the security of information and the privacy of senders and recipients. 1)高价值市场。将高价值商品进行数字化之后,记录在区块链上,进行资产所有权的维护。 1) High-value markets. After digitizing high-value commodities, they are recorded on the block chain for the maintenance of ownership of assets. 2)资产所有权交易。资产进行数字化之后,记录在区块链上,进行资产交易过程的记录管理。 2) An asset ownership transaction. After the asset is digitized, it is recorded on the block chain and records are managed in the course of the asset transaction. 3)共享数据场景。行业中共享数据的参与方,以区块链账本的形式进行记录这些共享数据。 3) Sharing of data scenes. Participants in the industry sharing of data record these shared data in block chain books. 4)合规审计。区块链对企业内部和之间进行的交易进行不可篡改可追溯的数据记录,合规审计工作需要这些高质量数据的输入,因此在技术上可以做到更加迅速高效。 (4) Compliance audits. The blocks chain makes it possible to record transactions within and between enterprises without tampering with traceable data, and compliance audits require the entry of such high-quality data, thus making it technically more expeditious and efficient. 下面我针对上述四种类型分别举例现实环境中可以落地的四个业务场景。 I would like to refer to four business scenarios that can be found in the real environment for each of these four types. 场景一:快递保价 scene one: Express delivery premium 围绕保价场景,快递公司进行商品运输,保险公司提供商品保价,商家提供商品销售,卖家购买保价服务,政府进行行业监管。 In the context of price-fixing scenarios, couriers transport goods, insurance companies provide commodity price guarantees, merchants provide commodity sales, sellers buy price-fixing services, and the Government regulates the industry. 那么,要把哪些东西记录在区块链上呢?有几个关键的点,商品的物流详情、账户、身份、理赔、其他参考数据等信息记录在区块链上。 So, what is to be recorded on the block chain? There are several key points, and the logistics details of the commodity, the accounts, the identity, the settlement of claims, other reference data, etc. are recorded on the block chain. 保价就是合约的概念,当客户对包裹进行正常签收后,自动触发账户理赔,合约正常结束,保费自动清算结束。如果出现问题件或者遗失件的时候,触发保险公司理赔流程。 The premium is the concept of the contract, which triggers the settlement of the account when the customer properly signs the package, the conclusion of the contract, and the liquidation of the premium. 场景二:公益快递 scene two: a public service delivery 针对公益活动,比如「一分钱」活动,从每个公益包裹的费用中拿出一分钱捐赠给公益组织的账户。此场景中,快递公司依然承担商品运输,公益组织提供公益活动执行,扶贫商家提供公益扶贫商品销售等。 For public goods, such as "one penny" activities, a fraction of the cost of each package is donated to the accounts of public goods organizations. In this scenario, couriers are still responsible for the transportation of goods, public goods organizations provide public goods for implementation, and pro-poor businesses provide pro-poor goods for sale, among other things. 那么区块链里记录的就是商品的物流详情,包裹签收后就会记录到区块链上,自动触发从物流公司的公益账户转移到公益组织的账户上。当公益活动结束后,整个流程是公开透明的,避免了大众对社会公益活动的不信任感。 Then what is recorded in the block chain is the logistics details of the commodities, and when the parcels are signed, they are recorded on the block chain, triggering an automatic transfer from the public interest account of the logistics company to the account of the public interest organization. When the public good is over, the process is open and transparent, avoiding public distrust of the social good. 场景三:行业黑名单共享 scene three: industry blacklist sharing 快递从业人员的黑名单,目前来看还是线下模式为主。我们希望通过区块链技术,让每个公司将从业人员黑名单记录到区块链上,其他公司也可以查询,而且数据不可以被修改,并能够追溯到这个人是在哪家公司做了什么样的不恰当行为等信息。 The blacklists of couriers are still largely offline. Through block chain technology, we want each company to record blacklists of practitioners on block chains, and other companies can search them, and the data cannot be modified, and we can trace information about where the person has done some inappropriate behavior. 场景四:邮政寄递渠道安全事件监管 scene 4: Postal channel security incident monitoring 很多快递公司会装上安检机,政府也想知道每家物流公司有没有运输安全隐患事件。通过分布式记账的模式,让各个快递公司在出现安全事件时,将安全事件的有效信息记录于区块链上,使得监管机构可以实时监控且不可篡改。 Many couriers will be installed on security machines, and the government would like to know whether each logistics company has a transport security risk. Through a distributed accounting model, individual couriers will be able to record valid information about security incidents on the block chain in the event of a security incident, allowing regulators to monitor them in real time and not to alter them. 如何在快递物流行业内推广应用区块链 how to promote the application of block chains within the express delivery logistics industry 关于如何在快递物流行业内推广应用区块链,我有三个建议: I have three recommendations on how to promote the application of block chains within the express delivery logistics industry: 1)制定标准:面向物流快递行业的区块链应用框架和业务场景。怎么把一个技术用好?要关注技术和业务的结合,而不是为做区块链技术而做,忘记了做事情的本来目标。 1) Standard-setting: A framework for the application of block chains and business scenes for the logistics express industry. How can a technology be used? Focus on the combination of technology and business, rather than on block-chain technology, forgetting the original goal of doing things. 2)教育培训:对物流快递行业从业者进行普及和宣传。针对从业者结合我们的业务场景,做区块链技术的培训和宣传。 (2) Educational training: promote awareness and awareness-raising among operators in the logistics express industry. 3)对话交流:提供沟通平台进行常态化信息交流。 3) Dialogue exchange: provide a communication platform for regular information exchange.
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群
















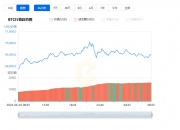
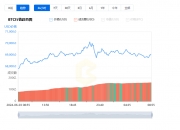
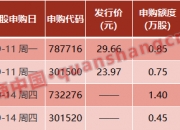


发表评论